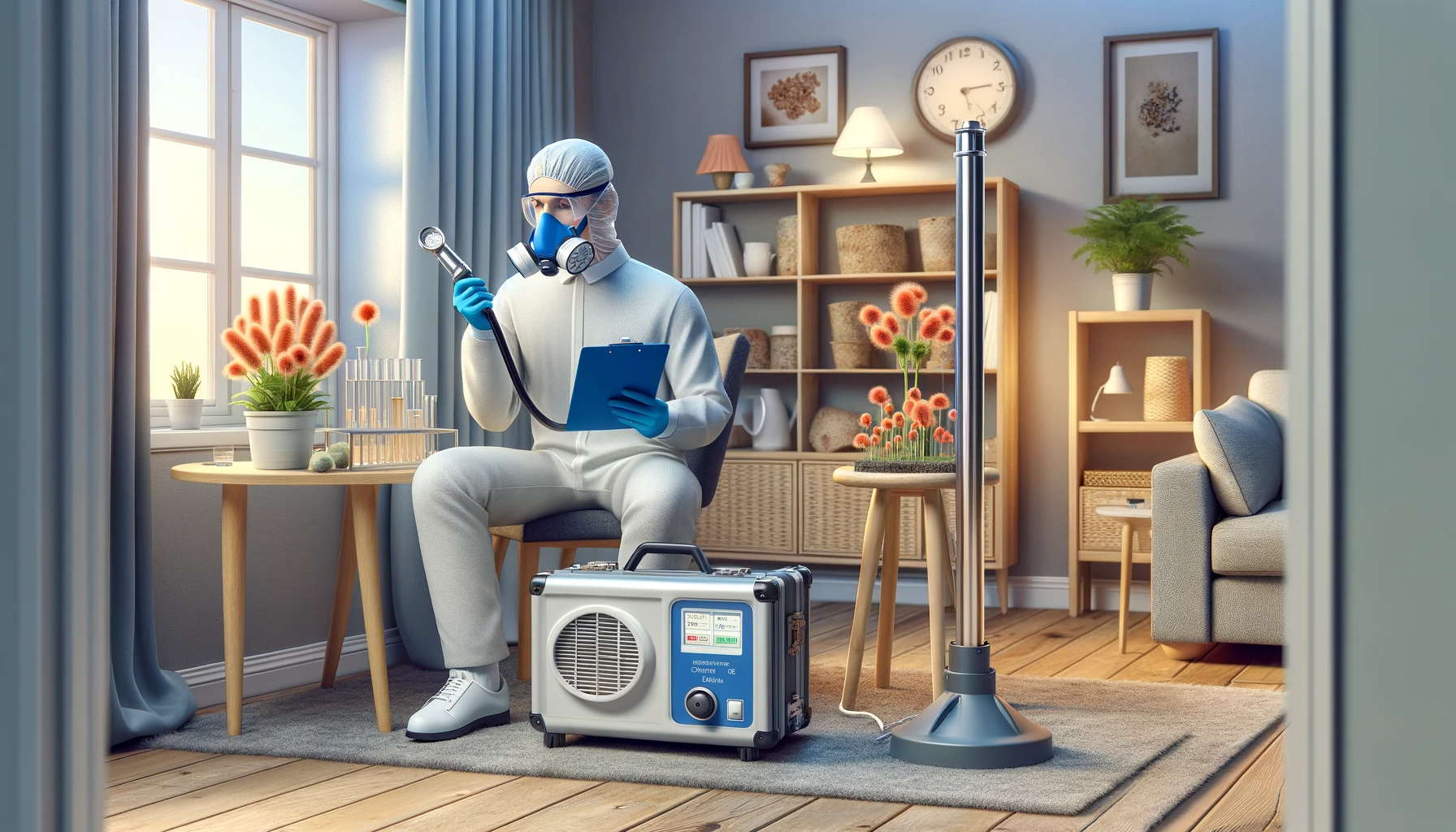
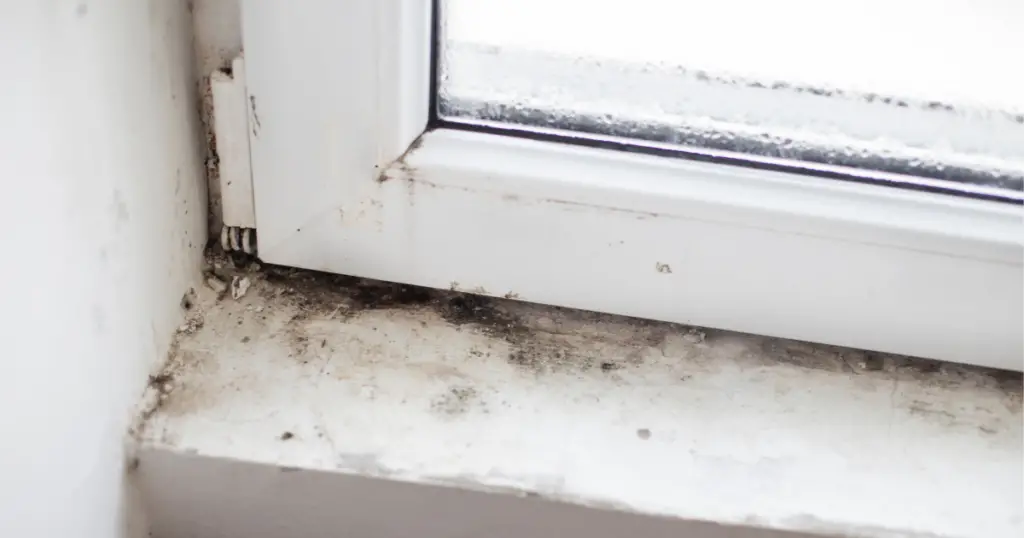
Mold is a type of fungus that can be found both indoors and outdoors, with some species being more dangerous than others. The health risks associated with mold are often underestimated. Mold spores, which can become airborne and spread rapidly, cannot be seen by the naked eye – however, that does not mean it’s absent from your home!
Humidity and water damage are the perfect conditions in which mold and mildew can flourish, whether it’s in your bathroom, attic, basement or other wet areas. These fungi are commonly found after condensation build-up, leaks or floods occur.
If you suspect mold growth in your home, testing for contamination should be done promptly.
Property owners must diligently identify and address humidity issues, as they are not always visible. Hidden behind walls and beneath carpets, undetected moisture problems can become the breeding ground for black mold contamination if left untreated.
Not only can prolonged exposure to black mold exacerbate existing respiratory problems such as asthma and allergies, but it also may cause more severe conditions like chronic bronchitis, neurological difficulties, cancer and even heart ailments.
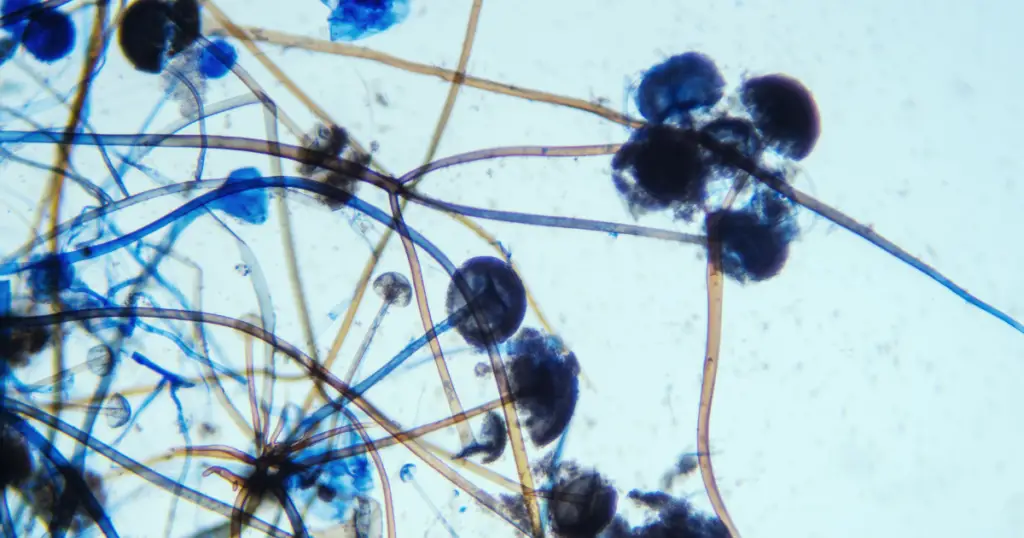

What are Mold Spores and Mycotoxins?
Mold spores and mycotoxins are part of the fungi family. Mold spores are microscopic particles that can be released into the air and transported by wind, water droplets, and animals.
Mycotoxins are toxic substances produced by certain types of mold. Mold spores and mycotoxins can cause various health issues for humans, such as respiratory conditions, skin irritations, neurological problems, and even cancer. It is important to avoid exposure to mold spores and mycotoxins when possible as even small amounts can lead to long-term health issues.
How Common Is Mold & Where Can I Find It?
Mold is a common problem that affects many homes and businesses. They are everywhere, from the walls and ceilings to carpets, furniture, and draperies. Mold is an essential part of the environment, as it helps to break down organic compounds and recycles nutrients into new materials. However, when these toxins become airborne, they can be dangerous.
Have you been smelling a musty odor with seemingly no visible signs of mold (such as black, white or brownish color)? The mold has likely spread to areas not easily seen by the eye. To help detect such hidden growths, it is recommended to test for mold in these common yet often overlooked sites, such as:
- Underneath stacks of newspapers or cardboard;
- Inside wall stud spaces that contain plumbing lines hidden within drywall;
- Under sinks and around leaking windows covered by wallboard;
- Inside ventilation ducts and beneath carpets that were once wet due to flooding or carpet cleaning activities;
- Behind your refrigerator;
- On the backside of acoustic ceiling tiles if there has been roof leakage present before, and anywhere else where water damage was exposed.
How do molds get in the indoor environment?
Mold can be found both inside and outside homes. It can enter through open doorways, windows, vents, and heating and air conditioning systems. Not only can mold attach to clothing and shoes when you’re outside but it can also be brought inside on pets.
It can also be transported through dust, and travel on air currents and water droplets. Mold thrives in warm, damp conditions, making it even more prone to grow in areas such as the bathroom or basement. Also, mold spores are often present in newly constructed buildings due to materials that did not completely dry before being sealed up.
What is Indoor Air Quality Testing?
Indoor air quality testing is the process of collecting and analyzing samples from the air inside a building to evaluate the levels of airborne pollutants. Testing for mold and other airborne toxins can detect both active growths as well as contaminated areas that could pose health risks over time.
The results of an air quality test for mold will tell you if any harmful spores are present, as well as what type of is present in the air. It can also give you more information about the spores’ size, shape, and chemical composition. Being aware of your indoor air quality allows you to make informed decisions on ways to improve air quality and reduce your risk and exposure to toxic mold and its health risks.
Having indoor air quality mold testing conducted is highly recommended if you experience the signs of mold or suspect that there may be a problem in your home or workplace.
Air-Sampling Devices
When it comes to detecting mold, there are numerous instruments available for air sample collection and analysis. Popular models include:
- impaction samplers that use a calibrated air pump to impact spores onto a prepared microscope slide;
- cassette samplers, This system may use disposable or single-use components and rely on a forced air process to blow spores onto the collection media;
- airborne-particle collectors trap spores directly on a culture dish. By utilizing these tests, you can accurately determine the exact species of mold present.
Types of Air Sample Testing
To accurately assess indoor air quality, air sampling is one of the most effective methods available. Specifically, there are two primary mold tests: viable and non-viable.
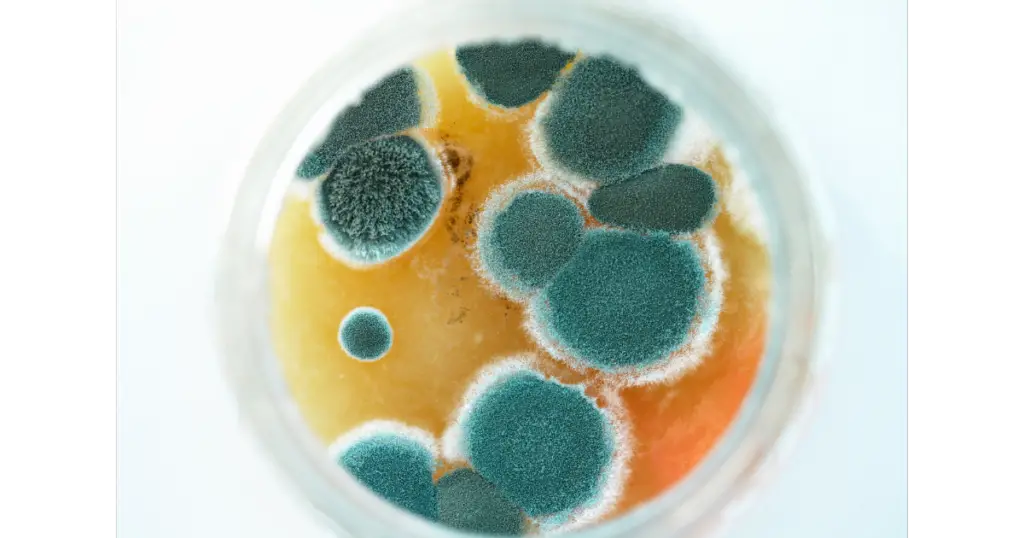
Viable Test – To accurately identify the species and genus of airborne microorganisms, a sample is taken on a growth media and then cultured in a petri dish. As colonies form over time, this procedure will divulge what type of microbial life exists within the air sample. With thousands of mold species in existence, some more hazardous than others, it is essential to identify which types are present. Viable air sampling provides this key information, helping ascertain if you may be exposed to toxic molds.
Non-viable testing – Non-viable tests, or spore traps as they’re better known, have become the industry standard for residential mold testing. With this method of air sample collection, no culturing is necessary – meaning results are available much faster than with traditional methods.
Pros and Cons of Viable and Non-Viable Testing
Both types of tests offer unique advantages and drawbacks. Viable tests require more equipment and expertise but can provide an accurate count of the types and numbers of fungi present in an area. Non-viable tests are simpler but do not give as detailed results, making it difficult to determine exact levels of contamination. Regardless, both methods can be useful tools for identifying potential mold problems.
At-Home Test Kit
Although you can find mold testing kits in home improvement stores and online, be aware that not all kits are created equal. Some only show whether there is mold present on surfaces or not. The entire testing process will take a few days to finish, if the initial results indicate occasional spreading of spores; then the best next move would be sending it off to an accredited lab for further evaluation and verification of what type of microorganism it actually is.

How to use it?
- Close the contaminated area- Close the windows and doors in the room you will be testing 24 hours before performing the test. This allows potential mold spores to congregate without being disturbed by drafts.
- Set up the kit- Take out the kit’s materials from their packaging. You should be able to observe a shallow plastic or glass petri dish with its lid and label. The inside of the petri dish is pre-treated using “microbial culture,” which stimulates mold spores’ growth. This method allows you to quickly and effectively gather a sufficient sample size within the manufacturer’s timeframe for mold testing.
- Let the petri dish sit undisturbed for a few days- Carefully take off the lid and place it face up on a flat surface. Leave the petri dish alone for 48 hours, although this may differ slightly depending on what your manufacturer has instructed you to do. If possible, restrict traffic in that room while testing is being conducted not to disrupt any airflow.
- Securely shut the petri dish and store it in a dark area.- After the designated time has expired, reattach the lid to the petri dish and secure it by wrapping a layer of tape around its edges. Scotch or electric tape are safe options for this purpose; however, try to keep away from duct tape as they can be troublesome when you want to take them off later. Take the label included in your kit and mark it with today’s date. After that, secure the label to the bottom of dish and enclose it using tape. Lastly, store it somewhere dark like a dresser drawer or shelf of a closet for optimal results.
- Monitor the dish for any signs of mold growth. In two days, inspect the petri dish for signs of mold; it will look similar to what you’d discovered on your refrigerator’s stale food. If any growth is detected, this would confirm that mold has developed within the dish.
- If the petri dish is free of signs of mold growth, return it to its dark spot and check again in 24 hours. After five days have passed since the label date (five total days), if your mold testing has yielded nothing, you can discard the dish with confidence—the kit did not detect any presence of mold in that room!
- If your test reveals mold, you can submit it to a lab recommended by the manufacturer. This will identify the mold type and how best to handle it. Most kits come with an envelope for mailing as well as payment instructions for analysis.
What are the Other Types Of Mold Testing?
Even though not as common, other types of testing can provide more specific results, such as:
- Surface Testing – Surface testing is used to determine the presence of mold on a particular surface. Using swabs and/or tape lifts, samples are taken from various surfaces throughout the house or workplace to analyze for fungal contaminants.
- Mycotoxin testing – This test looks for mycotoxins, toxic substances a mold produces. To get an accurate reading of the mycotoxin levels, samples from multiple areas must be taken and then sent to a lab for analysis.
- Endotoxin (Also done by Envirobiomics) – Endotoxins are a detrimental ingredient found within the membranes of Gram-Negative bacteria (GNB), which can be present in any natural setting. These toxins don’t even have to remain active and alive since both viable and non-viable GNB contribute endotoxins. Recently, it was uncovered that these harmful particles play a major role in Chronic Inflammatory Response Syndrome cases – an alarming discovery for many.
- ERMI (Environmental Relative Moldiness Index) – To ensure accuracy and reliability, this test is conducted by a specialized lab called Envirobiomics. ERMI utilizes an impartial, standardized genetic-based testing process to recognize and measure molds effectively. This is a test that gives a numerical value for the types and amount of mold spores present in indoor air. This testing is useful to compare the results of one home to another, or when comparing a space before and after remediation. ERMI will give you an index score, with higher values indicating greater amounts of mold.
- HERTSMI-2 (Health Effects Roster of Type-Specific Formers of Mycotoxins and Inflammagens) – HERTSMI is an additional testing process utilized by Envirobiomics to detect levels of harmful toxins created by mold. By utilizing a sample from the home, HERTSMI can help analyze the types and concentrations of mycotoxins in the air or any surface within your residence. This data will provide a much better understanding of potential health risks and effects.
Specific Recommendations to limit mold growth:
- Try to keep humidity levels low throughout the day, ideally between 30% and 50%. An air conditioner or dehumidifier will help you keep the level low. Because humidity levels depend on temperature and moisture, it’s important to check the humidity level multiple times a day.
- Use an air conditioner or a dehumidifier during humid months.
- Good ventilation is key in any home. Be sure to use exhaust fans to vent air outside. Vents are effective in the kitchen and bathroom; ensure your clothes dryer also vents outside.
- Fix leaks in your home’s roof, walls, or plumbing, so mold does not have moisture to grow.
- Consider not using carpet in rooms or areas like bathrooms or basements that may have a lot of moisture.

Professional Help
When it comes to mold testing, seeking professional help can be invaluable. Expert technicians can identify and quantify different species of mold in the air as well as measure overall air quality.
Professional testing and consulting services can provide valuable insight into the severity of a specific mold problem and recommend appropriate steps for mold remediation.
Furthermore, they will also help ensure that proven protocols are followed and that all necessary safety measures are taken to restore indoor air quality.
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]